Consequently a further favourable variance of $1,200 is recorded for efficiency reasons (the company was efficient because it produced 6,000 standard hours worth of product in 5,400 hours). Assume a company budgeted to produce 1,000 units of product in 5,000 labour hours (each unit therefore taking 5 standard hours of labour). Fixed overhead efficiency variance is the difference between the number of hours that actual production should have taken, and the number of hours actually taken (that is, worked) multiplied by the standard absorption rate per hour. Fixed overhead volume variance is the difference between actual and budgeted (planned) volume multiplied by the standard absorption rate per unit. Calculate the fixed overhead spending and production volume variances using the format shown in Figure 10.13 “Fixed Manufacturing Overhead Variance Analysis for Jerry’s Ice Cream”.
Accounting Ratios
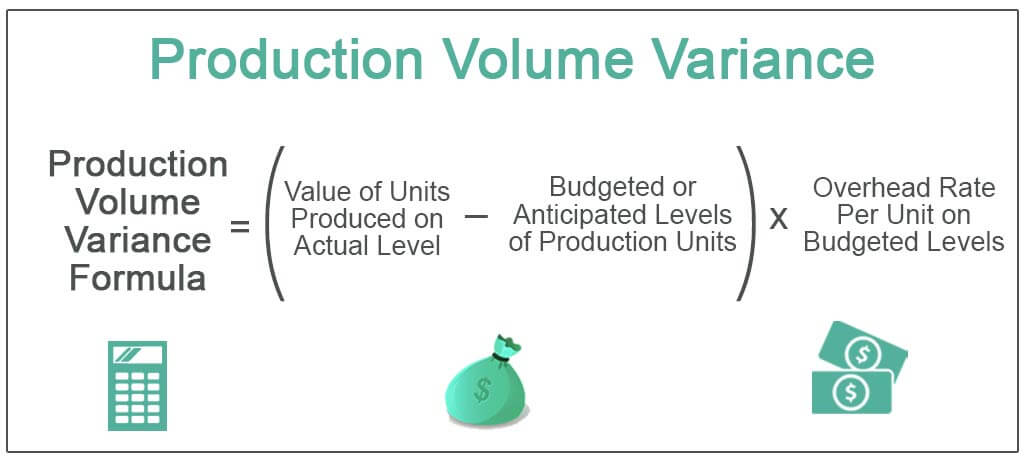
Fixed overhead volume variance is defined as the difference between the budgeted fixed overhead and the fixed overhead applied to actual output. This variance arises when there is a discrepancy between the actual number of units produced and the number expected to be produced at a given level of fixed overhead costs. If the fixed overhead cost applied to the actual production using the standard fixed overhead rate is bigger than the budgeted fixed overhead cost, the fixed overhead volume variance is the favorable one.
How to Calculate and Analyze Gross Profit Ratio
Figure 10.14 summarizes the similarities and differences betweenvariable and fixed overhead variances. Notice that the efficiencyvariance is not applicable to the fixed overhead varianceanalysis. The significance of fixed overhead volume variance extends beyond mere number-crunching; it influences strategic decision-making and long-term planning. By shedding light on potential inefficiencies and providing a basis for corrective action, it plays an integral role in shaping a company’s financial health and competitive stance. An overhead cost variance is the difference between how much overhead was applied to the production process and how much actual overhead costs were incurred during the period.
- The variance arises due to a change in the level of output attained in a period compared to the budget.
- It is important for businesses to analyze these factors thoroughly to understand the causes of variances and to implement measures to optimize production processes and capacity utilization.
- It requires a forward-looking approach where past variance data informs future operational and financial strategies.
- This is due to the actual production volume that it has produced in August is 50 units lower than the budgeted one.
Related AccountingTools Course
This is a portion of volume variance that arises due to high or low working capacity. It is influenced by idle time, machine breakdown, power failure, strikes or lockouts, or shortages of materials and labor. The graph shows that absorption costing takes what is a fixed cost ($10,000 per year), and converts it to a cost per unit of activity, effectively treating it as a variable cost ($10 per unit). The net variance from standard cost and the line items leading up to it build deviations from standard amounts right into the income statement.
At the same time actual overhead is lower than budgeted, also leading to over absorption. Graph 4 shows a situation where both actual activity and actual overhead expenditure differ from budget. In this example, assume the selling price per unit is $20 and 1,000 units are sold.
This is the portion of volume variance that is due to the difference between the budgeted output efficiency and the actual efficiency achieved. In practice other measures of activity, in particular direct labour hours (DLHs), are used as an absorption base. Costing system wherein fixed manufacturing overhead is allocated to (or absorbed by) products being manufactured. This system, which treats fixed manufacturing costs as a product cost, is required for external financial statements. The variable factory overhead controllable variance indicates how well the company was able to adhere to the budget.
Our mission is to empower readers with the most factual and reliable financial information possible to help them make informed decisions for their individual needs. Our writing and editorial staff are a team of experts holding advanced financial designations and have written for most major financial media publications. Our work has been directly cited by organizations including Entrepreneur, Business Insider, Investopedia, Forbes, CNBC, and many others. Finance Strategists is a leading financial education organization that connects people with financial professionals, priding itself on providing accurate and reliable financial information to millions of readers each year.
The standard cost per unit of $113.60 calculated previously is used to determine cost of goods sold – at standard amount. Similarly, if the allocated volume is down to the number of machine hours and a company outsources some or all of its production, the budgeted amount of machine hours will be much less than expected. Fixed overhead total variance is the difference between fixed overhead incurred and fixed overhead absorbed. The volume efficiency variance is calculated in the same way as the labour efficiency variance. This example provides an opportunity to practice calculating the overhead variances that have been analyzed up to this point.
The volume capacity variance is the difference between the budgeted hours of work and the actual active hours of work (excluding any idle time). When the cumulative amount of the variance becomes too large over time, a business should alter its budgeted allocation rate to bring it more in line with actual volume levels. This type of variance is calculated separately for direct variable expenses and overhead 1 period non-manufacturing costs are classified into two categories variable expenses. Answer 2 was the most popular of the wrong answers, which suggests that candidates understood that situation (1) leads to over absorption and that it was situation (2) that caused the problem. If actual hours worked are below budget then by applying the predetermined absorption rate (which is based on budgeted hours) to this lower number of actual hours will lead to under absorption.
Nonetheless, we will assign the fixed manufacturing overhead costs to the aprons by using the direct labor hours. Fixed manufacturing overhead costs remain the same in total even though the production volume increased by a modest amount. For example, the property tax on a large manufacturing facility might be $50,000 per year and it arrives as one tax bill in December. The amount of the property tax bill did not depend on the number of units produced or the number of machine hours that the plant operated.
The $5 fixed rate plus the $7 variable rate equals the $12 total factory overhead rate per direct labor hour. Fixed overhead efficiency variance is the difference between absorbed fixed production overheads attributable to the change in the manufacturing efficiency during a period. The fixed overhead costs included in this variance tend to be only those incurred during the production process, such as factory rent, equipment depreciation, staff salaries, insurance of facilities and utility fees.