This variance would be posted as a credit to the fixed overhead budget variance account. The amount of expense related to fixed overhead should (as the name implies) be relatively fixed, and so the fixed overhead spending variance should not theoretically vary much from the budget. However, if the manufacturing process reaches a step cost trigger point where a whole new expense must be incurred, this can cause a significant unfavorable variance. Also, there may be some seasonality in fixed overhead expenditures, which may cause both favorable and unfavorable variances in individual months of a year, but which cancel each other out over the full year. Other than the two points just noted, the level of production should have no impact on this variance.
- Other than the two points just noted, the level of production should have no impact on this variance.
- For the past 52 years, Harold Averkamp (CPA, MBA) has worked as an accounting supervisor, manager, consultant, university instructor, and innovator in teaching accounting online.
- Costs such as direct material and direct labor, on the other hand, vary directly with each unit of output.
- As shown in the example above, Tahkila Industrial had a favorable variance for the year ended 2019 since they had to pay $80,000 less than expected.
- For example, factory rent, supervisorsalaries, or factory insurance may have been lower thananticipated.
Sales Quantity Variance: Definition, Formula, Explanation, And Example
The standard overhead rate is the total budgeted overhead of \(\$10,000\) divided by the level of activity (direct labor hours) of \(2,000\) hours. If Connie’s Candy only produced at \(90\%\) capacity, for example, they should expect total overhead to be \(\$9,600\) and a standard overhead rate of \(\$5.33\) (rounded). If Connie’s Candy produced \(2,200\) units, they should expect total overhead to be \(\$10,400\) and a standard overhead rate of \(\$4.73\) (rounded).
How do we calculate the total overhead cost variance?
Interpretation of the variable overhead rate variance is often difficult because the cost of one overhead item, such as indirect labor, could go up, but another overhead cost, such as indirect materials, could go down. Often, explanation of this variance will need clarification from the production supervisor. Another variable overhead variance to consider is the variable overhead efficiency variance. This variance would be posted as a debit to the fixed overhead volume variance account. The company can calculate fixed overhead volume variance with the formula of standard fixed overhead applied to actual production deducting the budgeted fixed overhead. This result of $950 of unfavorable fixed overhead volume variance can be used together with the fixed overhead budget variance to determine the total fixed overhead variance.
Variable Overhead Variance Analysis
Adam received his master’s in economics from The New School for Social Research and his Ph.D. from the University of Wisconsin-Madison in sociology. He currently researches and teaches economic sociology and the social studies of finance at the Hebrew University in Jerusalem. Double Entry Bookkeeping is here to provide you with free online information to help you learn and understand bookkeeping and introductory accounting. This means that they must have had an unexpected earning of $80,000 positively affecting the financial statements. Our mission is to empower readers with the most factual and reliable financial information possible to help them make informed decisions for their individual needs. Our writing and editorial staff are a team of experts holding advanced financial designations and have written for most major financial media publications.
Fixed Overhead Budget Variance
For the past 52 years, Harold Averkamp (CPA, MBA) hasworked as an accounting supervisor, manager, consultant, university instructor, and innovator in teaching accounting online. We will discuss how to report the balances in the variance accounts under the heading What To Do With Variance Amounts. For the past 52 years, Harold Averkamp (CPA, MBA) has worked as an accounting supervisor, manager, consultant, university instructor, and innovator in teaching accounting online. Chartered accountant Michael Brown is the founder and CEO of Double Entry Bookkeeping. He has worked as an accountant and consultant for more than 25 years and has built financial models for all types of industries. He has been the CFO or controller of both small and medium sized companies and has run small businesses of his own.
Formulas to Calculate Overhead Variances
Let’s assume it is December 2022 and DenimWorks is developing the standard fixed manufacturing overhead rate for use in 2023. As mentioned above, we will assign the fixed manufacturing overhead on the basis of direct labor hours. Fixed overhead budget variance is one of the two main components of total fixed overhead variance, the other being fixed overhead volume variance. A favorable variance means that the actual hours worked were less than the budgeted hours, resulting in the application of the standard overhead rate across fewer hours, resulting in less expense being incurred. However, a favorable variance does not necessarily mean that a company has incurred less actual overhead, it simply means that there was an improvement in the allocation base that was used to apply overhead.
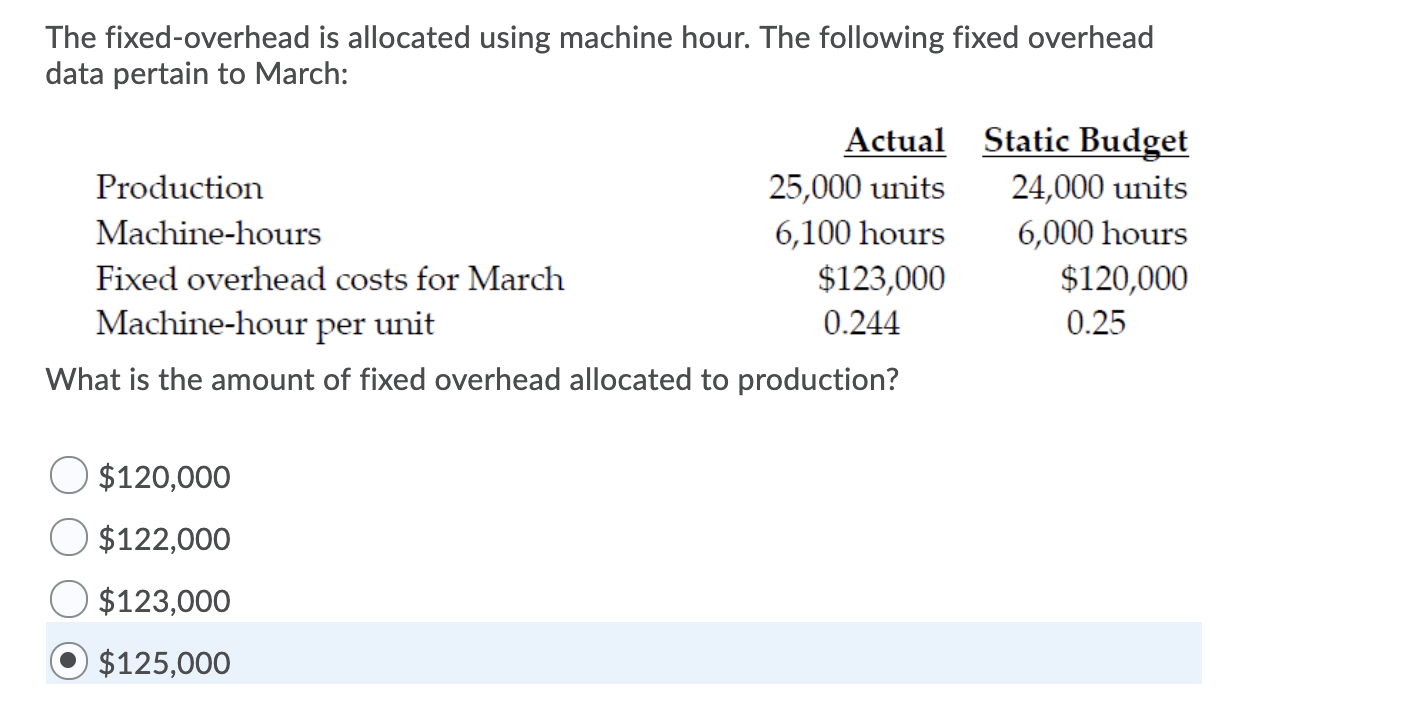
Likewise, if the actual production exceeds the normal capacity, the result is favorable fixed overhead volume variance and vice versa. However, as the name suggested, it is the fixed overhead volume variance that is more about the production volume. Likewise, we can also determine whether the fixed overhead volume variance is favorable or unfavorable by simply comparing the actual production volume to the budgeted production volume. Recall that the fixed manufacturing overhead costs (such as the large amount of rent paid at the start of every month) must be assigned to the aprons produced. In other words, each apron must absorb a small portion of the fixed manufacturing overhead costs. At DenimWorks, the fixed manufacturing overhead is assigned to the good output by multiplying the standard rate by the standard hours of direct labor in each apron.
The following information is the flexible budget Connie’s Candy prepared to show expected overhead at each capacity level. Budget or spending variance is the difference between the budget and the actual cost for the actual hours of operation. This variance can be compared to the price and quantity variance developed for direct materials and direct labor. Using the information given below, compute the fixed overhead cost, expenditure, and volume variances. Therefore, these variances reflect the difference between the standard cost of overheads allowed for the actual output achieved and the actual overhead cost incurred.
This system, which treats fixed manufacturing costs as a product cost, is required for external financial statements. In case of fixed overhead, the budgeted and flexible budget figures are exactly the same. Fixed overheads are a line item in our variance analysis because a fixed overhead what is a post closing trial balance definition meaning example is not supposed to vary, as the name suggests. This example provides an opportunity to practice calculating the overhead variances that have been analyzed up to this point. In this case, the variance is favorable because the actual costs are lower than the standard costs.
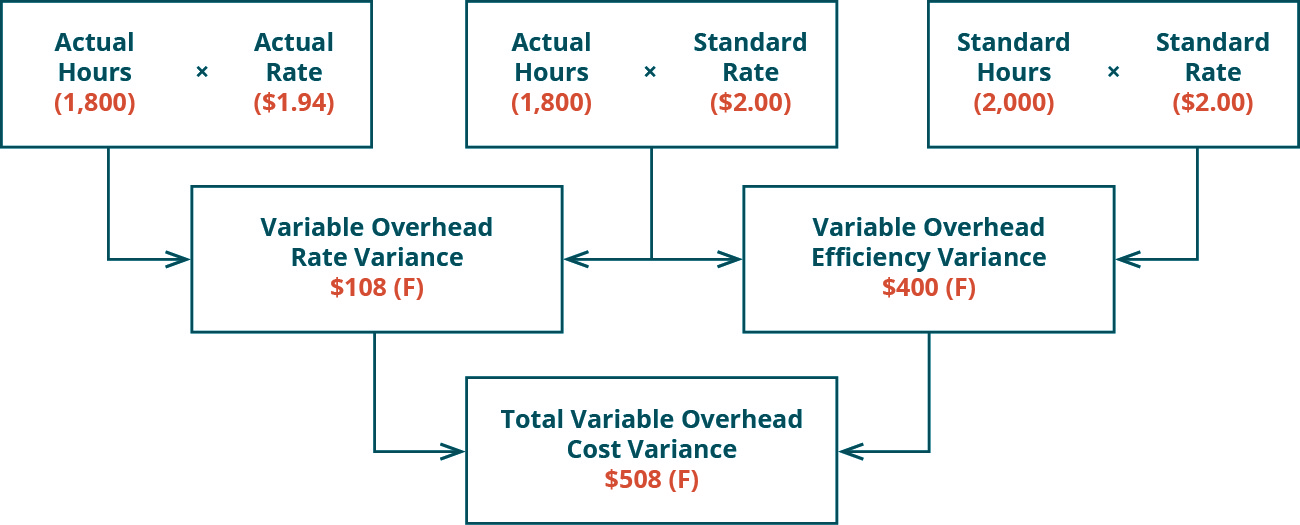
Figure 8.5 shows the connection between the variable overhead rate variance and variable overhead efficiency variance to total variable overhead cost variance. An unfavorable or adverse fixed overhead spending variance would arise when the actual fixed overheads exceed the budgeted fixed overheads. Standard fixed overhead rate can be calculated with the formula of budgeted fixed overhead cost dividing by the budgeted production volume. The budgeted production volume here is also referred to as the normal capacity of the company or the existing facility in the production.
The standard overhead rate is the total budgeted overhead of $10,000 divided by the level of activity (direct labor hours) of 2,000 hours. Notice that fixed overhead remains constant at each of the production levels, but variable overhead changes based on unit output. If Connie’s Candy only produced at 90% capacity, for example, they should expect total overhead to be $9,600 and a standard overhead rate of $5.33 (rounded).